difference between unit operation and unit process
Unraveling the Enigmatic Distinction: Unit Operation vs. Unit Process in Chemical Engineering
Introduction to Unit operation and process
Chemical engineering plays a pivotal role in transforming raw materials into valuable products that enrich our lives. Two fundamental concepts integral to the field are “unit operation” and “unit process.” While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct aspects of chemical engineering that perform specific functions in the production and transformation of substances. In this article, we will delve into the details of unit operations and unit processes, highlighting their differences and significance in the realm of chemical engineering.
what is difference between unit operation and unit process
Unit Operation: The Building Blocks of Chemical Engineering
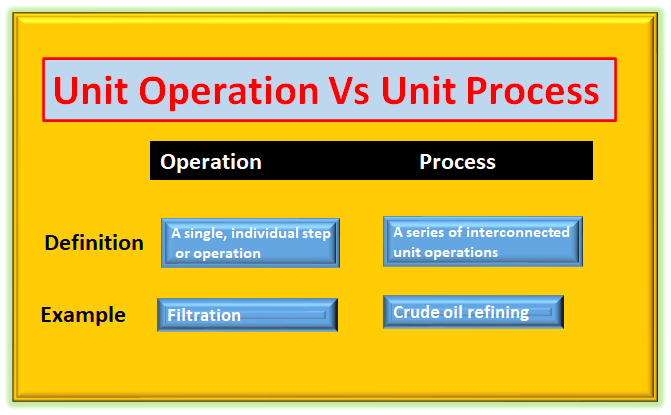
Unit operations are the foundational building blocks of chemical engineering processes. These operations involve the physical transformation or separation of substances, typically without any significant chemical change occurring. They are essential steps in various chemical processes and are often combined to create complex operations that lead to the desired end products, what is difference between unit operation and unit process.
Key Characteristics of Unit Operations:
- Physical Transformations: Unit operations are primarily concerned with physical changes in the materials being processed. Examples include mixing, crushing, filtration, distillation, crystallization, evaporation, and absorption.
- No Chemical Alteration: During unit operations, the chemical composition of the substances remains unchanged. The focus is on modifying the physical properties such as size, shape, density, or phase of the components.
- Reversibility: Most unit operations are reversible, meaning the process can be undone, and the original materials can be retrieved, making them valuable in recycling and waste treatment.
- Individual Processes: Unit operations are standalone processes that can be applied to a wide range of chemical systems, making them versatile and adaptable.
Examples of Unit Operations
i. Distillation: Separation of components in a mixture based on their different boiling points.
ii. Filtration: Removal of solid particles from a liquid or gas using a porous medium.
iii. Mixing: Combining two or more components to achieve uniformity.
iv. Crystallization: Formation of crystals from a solution to purify substances.
v. Evaporation: Removal of a solvent to concentrate a solution or separate components.
Above are noting but Examples of Unit Operations. I hope you got celerity of Examples of Unit Operations.
Unit Process: The Integrated Chemical Transformations
Unit processes, on the other hand, are chemical reactions or operations that lead to a significant chemical change in the raw materials. Unlike unit operations, unit processes involve breaking or forming chemical bonds, resulting in the creation of entirely new substances or the alteration of existing ones.
Key Characteristics of Unit Processes
- Chemical Transformations: Unit processes bring about chemical changes in the substances being processed. They involve chemical reactions and conversions.
- Irreversibility: Unlike unit operations, unit processes are often irreversible, as the chemical reactions lead to the formation of new compounds or products.
- Specific to the Reaction: Each unit process is tailored to a specific chemical reaction or set of reactions, and they are not as versatile as unit operations.
- Inherent Energy Change: Since chemical reactions involve bond breaking and formation, unit processes may require energy input or release energy as a result, Examples of Unit Operations.
Examples of Unit Processes
i. Oxidation: A chemical reaction where a substance loses electrons or gains oxygen.
ii. Hydrogenation: The addition of hydrogen to a compound.
iii. Polymerization: The joining of monomers to form a polymer.
iv. Combustion: The reaction of a substance with oxygen, typically producing heat and light.
v. Fermentation: A process in which microorganisms convert sugars into alcohol or organic acids.
unit operation and unit process
Table summarizing the differences between unit operations and unit processes in chemical engineering.
| Aspect | Unit Operation | Unit Process |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical transformations or separations without significant chemical change. | Chemical reactions leading to new substances or chemical alterations. |
| Type of Change | Involves only physical changes (e.g., mixing, distillation, filtration). | Results in chemical changes (e.g., oxidation, polymerization, fermentation). |
| Reversibility | Generally reversible, original materials can be retrieved. | Typically irreversible, new substances are formed. |
| Focus | Modification of physical properties (e.g., size, shape, phase). | Creation of new substances or chemical alterations. |
| Example Processes | Distillation, Filtration, Mixing, Crystallization, Evaporation. | Oxidation, Hydrogenation, Polymerization, Combustion, Fermentation. |
| Energy Change | No inherent energy change, though energy may be required for the operation. | Inherent energy change due to chemical reactions. |
| Versatility | Highly versatile, can be applied to various chemical systems. | Specific to a particular chemical reaction or set of reactions. |
| Application Examples | Separation of components, concentration, purification. | Production of new chemicals, synthesis of compounds, conversion of raw materials. |
This table provides a concise overview of the key differences between unit operations and unit processes, highlighting their unique characteristics and significance in the field of chemical engineering.
People also ask
Question 1: What are unit operations and unit processes?
Answer: Unit operations and unit processes are fundamental concepts in chemical engineering. Unit operations refer to physical transformations or separations of substances without significant chemical changes, while unit processes involve chemical reactions that lead to the creation of new substances or chemical alterations , what is difference between unit operation and unit process.
Question 2: What is a unit operation and a unit process with an example?
Answer: A unit operation involves a physical change or separation of substances. For example, distillation is a unit operation that separates components in a mixture based on their different boiling points. Filtration is another unit operation that removes solid particles from a liquid or gas using a porous medium, what is difference between unit operation and unit process.
A unit process, on the other hand, involves chemical reactions. For example, fermentation is a unit process where microorganisms convert sugars into alcohol or organic acids. Another example is polymerization, which is a unit process that involves the joining of monomers to form a polymer.
Question 3: Which is a unit process?
Answer: A unit process is a chemical reaction or operation that leads to a significant chemical change in the raw materials. An example of a unit process is the reaction of oxidation, where a substance loses electrons or gains oxygen, resulting in a chemical alteration of the original material.
Question 4: How is a unit operation defined?
Answer: A unit operation is defined as a physical transformation or separation of substances without any significant chemical change occurring. These operations are essential steps in various chemical processes and are often combined to create complex operations that lead to the desired end products. Unit operations are generally reversible, and the focus is on modifying the physical properties of the components involved.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while unit operations and unit processes are both essential components of chemical engineering, they serve distinct purposes in the transformation of substances. Unit operations focus on physical changes and are reversible, making them widely applicable and flexible. On the other hand, unit processes involve chemical reactions and result in irreversible changes to the materials, paving the way for the creation of new products. Understanding the difference between these concepts is crucial for chemical engineers to design efficient and effective processes that lead to the production of a wide array of valuable products we use in our daily lives.
Read Also,
unit process and unit operation example
unit operation and unit process in pharmaceutical industry
what is unit operation and unit process
unit process in chemical industry pdf





2 thoughts on “difference between unit operation and unit process – Example, Importance & Application 3.2”
Comments are closed.